A Secure Network Requires Addressing IoT Security Complexity
- Technology Solutions
- 0 Replies
When organizations implement Zero Trust and SASE cybersecurity frameworks, the top priority is ensuring those connecting to the network are authenticated with appropriate access privileges. Users often represent the most fertile attack surface as they can go rogue or be phished, inadvertently sharing sensitive information with malicious actors that can cost a business dearly.
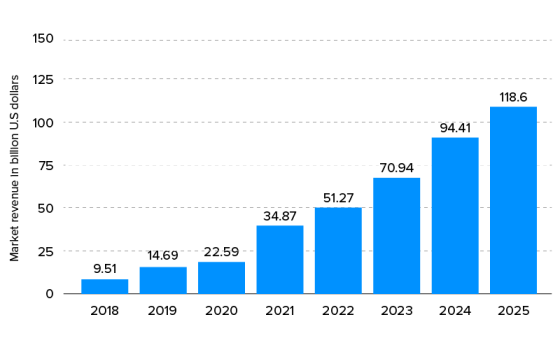
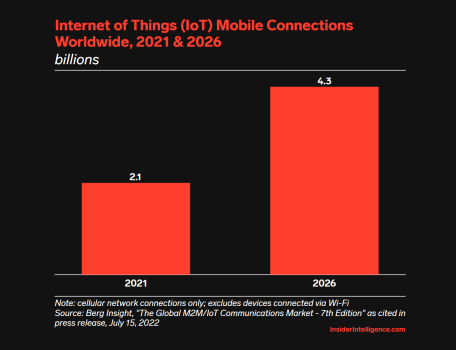
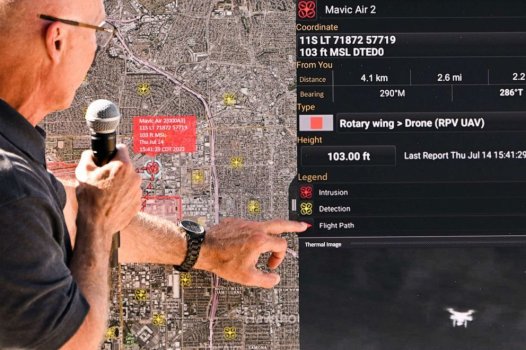
Meanwhile, organizations also must manage the flood of “things” entering the network, as in the Internet of Things (IoT). Sure, a wireless thermostat or smart speaker can’t be phished like a person, but each device represents another node that further expands the attack surface area, an area expanding at an exponential rate. Thankfully, recent communication from NIST National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) have helped to address this issue.
To summarize the findings, network and security teams face significant obstacles in securing IoT devices on the network. Dealing with IoT devices is just as complicated, if not more so, than managing users when tasked with safely and securely onboarding those devices onto the network while also monitoring them for optimal performance and protection.
Network Layer Onboarding and Lifecycle Management
NIST highlights in its project description how IoT security is difficult for myriad reasons:
Meanwhile, organizations also must manage the flood of “things” entering the network, as in the Internet of Things (IoT). Sure, a wireless thermostat or smart speaker can’t be phished like a person, but each device represents another node that further expands the attack surface area, an area expanding at an exponential rate. Thankfully, recent communication from NIST National Cybersecurity Center of Excellence (NCCoE) have helped to address this issue.
To summarize the findings, network and security teams face significant obstacles in securing IoT devices on the network. Dealing with IoT devices is just as complicated, if not more so, than managing users when tasked with safely and securely onboarding those devices onto the network while also monitoring them for optimal performance and protection.
Network Layer Onboarding and Lifecycle Management
NIST highlights in its project description how IoT security is difficult for myriad reasons:
- Manufacturers often provide a single set of log-on credentials for the millions of devices these organizations produce. Although sharing the same network credential for every device is often simple, this system lacks the ability to identify each device, nor is there a method to verify each device is connecting to the appropriate network.
- In contrast, manually provisioning a unique network credential for each device drastically increases the complexity of the on-boarding process, let alone that such approaches are resource intensive, error-prone, and insecure.
- Going further, requiring manufacturers to assign a unique network credential to each device as part of the manufacturing process is impractical and inefficient while potentially raising the cost of production.