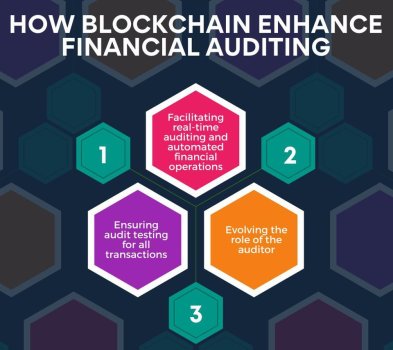
As a technology, blockchain comes with a few well-known qualities—tools based on the technology are impossible to breach, they store transactions and other records in real-time, the data stored in blockchains cannot be manipulated without authorization and many others. The common thread running through such characteristics is trust. Blockchain is, without a doubt, reliable for usage in several business areas. And that is why the technology, also known as a distributed ledger, has so many applications in fields as diverse as public welfare, supply chain-related functions and, of course, NFT transactions. Besides these, there are several uses of blockchain in financial services too. One of the prominent ones among them is financial auditing. Generally, major businesses may face difficulties in verifying the integrity of transactions, including all transactions of mega-corporations in audit tests and similar others. Using blockchain in financial services and functions such as auditing sorts out such problems for auditors and businesses everywhere.
Bringing in Real-Time Auditing and Automated Financial Operations
Traditionally, audits are supposed to be conducted at the end of a financial year. During that phase, trained auditors and chartered accountants run through, either partially or completely, thousands and thousands of transactions recorded throughout the year on balance sheets, cash flow statements and other financial documents to verify each entry for authenticity, understand the financial areas that are problematic within the organization and need correction and find instances of error and fraud, amongst other details.
With the increasing use of blockchain in financial services such as auditing, organizations could have their transactions verified and greenlit in real-time. This automation of auditing involves financial transactions going through audit scans as they take place. If an instance of fraud or error occurs, the financial directors and technical operators will get a notification about it. Then, such parties can conduct thorough financial investigations to get to the root of problematic situations. In such cases, computerized programs could settle blockchain-driven smart contracts on behalf of the concerned board of directors autonomously. Furthermore, blockchain could also enable automated payment processing to stakeholders, digital signing of documents and contracts, creating valid audit trails for transaction verification as well as registering digitized assets, which include stocks, NFTs, bonds, land titles.
Continue reading: https://www.forbes.com/sites/naveenjoshi/2022/03/03/making-financial-auditing-more-assured-with-blockchain/?sh=1b213a8f28de
Bringing in Real-Time Auditing and Automated Financial Operations
Traditionally, audits are supposed to be conducted at the end of a financial year. During that phase, trained auditors and chartered accountants run through, either partially or completely, thousands and thousands of transactions recorded throughout the year on balance sheets, cash flow statements and other financial documents to verify each entry for authenticity, understand the financial areas that are problematic within the organization and need correction and find instances of error and fraud, amongst other details.
With the increasing use of blockchain in financial services such as auditing, organizations could have their transactions verified and greenlit in real-time. This automation of auditing involves financial transactions going through audit scans as they take place. If an instance of fraud or error occurs, the financial directors and technical operators will get a notification about it. Then, such parties can conduct thorough financial investigations to get to the root of problematic situations. In such cases, computerized programs could settle blockchain-driven smart contracts on behalf of the concerned board of directors autonomously. Furthermore, blockchain could also enable automated payment processing to stakeholders, digital signing of documents and contracts, creating valid audit trails for transaction verification as well as registering digitized assets, which include stocks, NFTs, bonds, land titles.
Continue reading: https://www.forbes.com/sites/naveenjoshi/2022/03/03/making-financial-auditing-more-assured-with-blockchain/?sh=1b213a8f28de