K
Kathleen Martin
Guest
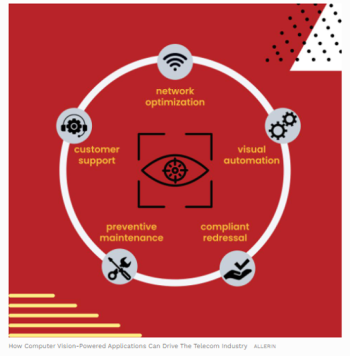
The global IoT telecom sector has grown to an astonishing figure of $17.67 billion in 2021 with a CAGR of 43.6% and the upward trend will continue for years to come. This is also because, unlike previously, when the telecom sector was limited to those who provided phone and internet services, the telecom industry has expanded across various sectors today, including broadband, mobile and the Internet of Things (IoT). As the customer base is rising exponentially and not just in the mobile or internet sectors, telecom service providers are capitalizing on the opportunity by using AI and the humongous trove of data that they have gathered for years. Computer vision for telecom can provide a better customer experience, improve operations, generate revenue, offer more products and services catered to what customers need, and draw actionable insights.
What is Computer Vision?
Just as how AI aids computers to think, Computer vision, as the name suggests, helps computers recognize objects and others via visual inputs. It uses AI, deep learning, algorithms like Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), and others to recognize objects in an image and video respectively.
Computer vision works similar to human vision, although the distinguishing factor here is that the latter has hundreds of thousands of years of context, while computer vision is still in its early stages and requires a huge trove of data to train over and over again in order to recognize objects, people, things, or others, including how far they are, if they are moving or not, and find anomalies, such as on an assembly line. But technically, there are hundreds of use cases of computer vision for telecommunication.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision uses a set of algorithms to work on the huge trove of data fed to it. The AI uses a model and compares it with the prediction until it recognizes the object. It uses deep learning and CNN for images, whereas RNN is used for moving images, i.e., videos, which are essentially a set of still images.
Continue reading: https://www.forbes.com/sites/naveenjoshi/2022/04/21/how-computer-vision-powered-applications-can-drive-the-telecom-industry/?sh=4bc3fe62620c
What is Computer Vision?
Just as how AI aids computers to think, Computer vision, as the name suggests, helps computers recognize objects and others via visual inputs. It uses AI, deep learning, algorithms like Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) and Recurrent Neural Network (RNN), and others to recognize objects in an image and video respectively.
Computer vision works similar to human vision, although the distinguishing factor here is that the latter has hundreds of thousands of years of context, while computer vision is still in its early stages and requires a huge trove of data to train over and over again in order to recognize objects, people, things, or others, including how far they are, if they are moving or not, and find anomalies, such as on an assembly line. But technically, there are hundreds of use cases of computer vision for telecommunication.
How Does Computer Vision Work?
Computer vision uses a set of algorithms to work on the huge trove of data fed to it. The AI uses a model and compares it with the prediction until it recognizes the object. It uses deep learning and CNN for images, whereas RNN is used for moving images, i.e., videos, which are essentially a set of still images.
Continue reading: https://www.forbes.com/sites/naveenjoshi/2022/04/21/how-computer-vision-powered-applications-can-drive-the-telecom-industry/?sh=4bc3fe62620c