K
Kathleen Martin
Guest
Welcome to the second post in our series on the challenges associated with the Internet of Things (IoT). In Part 1, An Ethical Hackers Guide to IoT Security Risks and Challenges, we took an in-depth look at the security risks and threats to IoT devices and systems, and we covered these IoT hacking methods and steps:
STAGE 4: Analyze the Firmware and Reverse Engineering
*Note: this example is taken from a book recommended in the resources section.
A great technique for compromising an IoT device involves downloading the firmware from the vendor’s download site(s). By getting access to the firmware binary, you can analyze it and extract it.
In this example, we look at a Netgear D6000 router firmware.
Download the firmware and extract the zip. You can then run a check on the file details:

Continue reading: https://securityboulevard.com/2021/12/an-ethical-hackers-guide-to-iot-security-risks-and-challenges-part-2/
- Stage 0: Pre-Engagement
- Stage 1: Passive Recon
- Stage 2: The Hardware – Opening the Devices and Discover What is Inside
- Stage 3: The Firmware Boot
- Stage 4: Analyze the Firmware and Reverse Engineering
- Stage 5: Flashing Firmware
- Stage 6: The Network and Radio Frequencies
STAGE 4: Analyze the Firmware and Reverse Engineering
*Note: this example is taken from a book recommended in the resources section.
A great technique for compromising an IoT device involves downloading the firmware from the vendor’s download site(s). By getting access to the firmware binary, you can analyze it and extract it.
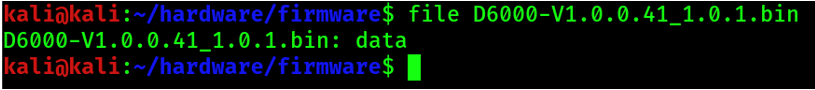
In this example, we look at a Netgear D6000 router firmware.
Download the firmware and extract the zip. You can then run a check on the file details:

Continue reading: https://securityboulevard.com/2021/12/an-ethical-hackers-guide-to-iot-security-risks-and-challenges-part-2/